
- Company overview The heart of SMC Vision & Philsophy Partnership Certifications Company culture
- Our service Design and Engineering Maintenance and Service Examine Production Line Upgrade and Transformation Storage and Logistics Processing, Trading and Distributor
- Management Our history Global responsibility Info Center
- Procurement center Internship
- Metal Steel Products Stainless Steel Products Aluminum Products Copper Products Galvanized Steel and PPGI Special Alloy Building Material
- Containers ISO Standard Container Equipment Container Storage Container Refrigerated/Reefer Container Offshore Container Container House Tank Container Container Fittings Container Trailer
- Gas Cylinder & Fire Extinguisher Cryogenic Liquid Cylinder Oxygen Gas Cylinder Storage Tank CNG Gas Cylinder LPG Gas Cylinder Hydrogen Gas Cylinder Nitrogen Gas Cylinder Industry Gas Cylinder Fire Extinguisher
- Metal Machinery Forming Machine Cutting Machine Processing Machine Bending Machine Block Machine Other Machinery Motor Spare Parts
- Mechanical Products Miscellany Mooring Equipment Marine Equipment Vehicle Industry Pressure Vessel Conveyor Belt Laser Equipment Bearing
- Electrical System Power Distribution Automation Electrical Cable Solar Power System Electric Protection System Transformer Production Line Lighting System
- Project Plastic Pipes and Pipe Fittings Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic Pontoon System
Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Strip For Oil Tank
Thickness: 0.125mm - 3.0mm
Width: As your request
Coil ID: 100mm/508mm
Specifications of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Strip:
1) Capacity: about 15,000 ton per month for steel strip/tape product
2) Thickness: from 0.125mm to 3.0mm, all available
3) Width: As your request
4) Grade: SGHC, Q195, SGCC, DX51D
5) Coil weight: from 50kg to 7000kg, all available
6) Coil ID: 100mm/508mm
7) Tensile strength: 28.1kgf/mm2 - 49.2kgf/mm2
8) Zinc coating weight: 30g/m2 - 600g/m2
9) Spangle: big spangle, normal spangle, small spangle, non-spangle
10) Surface treatment: chemical passivating treatment, oils, passivating + oils
11) Min. trial order 5ton each thickness, 1 x 20' per delivery
12) Surface Treatment of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Strip:

13) Spangle of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Strip:
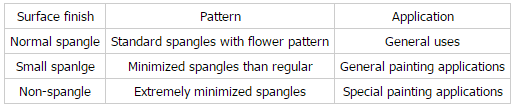
14) Features: Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Strip/Coil is manufactured to have a long durability, strong corrosion resistance and shiny surface.
It is also features excellent forming properties, paintability, weldability, and is suitable for fabrication by forming, pressing and bending.



Hot-dip galvanize can vary in appearance, and therefore usability, as a function of spangle size, zinc composition, mechanical treatment, and chemical or oiling treatments. Marketplace problems can develop because the customer finds the appearance is different than expected, or changes due to darkening, water staining, or field handling marks. These and other issues are reviewed, along with actions that can be taken to control them and minimize problems with end users.
Specifications of Prepainted Galvanized Steel Coil or Sheet:
1) Standard: ASTM A653, JIS G3312
2) Size: Thickness: 0.13-1.0mm, Width: 40mm - 1250mm
3) Zinc coating: 30g/m2 - 275g/m2; Top Coating: 15-25microns; Back Coating: 7-15microns
4) Colour: According to Customer's Sample or RAL Color Card
5) Package: Standard Export Package
6) Application: Production of Corrugated Steel Sheets, Decoration, Construction
Processing of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Strip
The process of hot-dip galvanizing results in a metallurgical bond between zinc and steel with a series of distinct iron-zinc alloys. The resulting coated steel can be used in much the same way as uncoated.
A typical hot-dip galvanizing line operates as follows:
Steel is cleaned using a caustic solution. This removes oil/grease, dirt, and paint.
The caustic cleaning solution is rinsed off.
The steel is pickled in an acidic solution to remove mill scale.
The pickling solution is rinsed off.
A flux, often zinc ammonium chloride is applied to the steel to inhibit oxidation of the cleaned surface upon exposure to air. The flux is allowed to dry on the steel and aids in the process of the liquid zinc wetting and adhering to the steel.
The steel is dipped into the molten zinc bath and held there until the temperature of the steel equilibrates with that of the bath.
The steel is cooled in a quench tank to reduce its temperature and inhibit undesirable reactions of the newly formed coating with the atmosphere.
Lead is often added to the molten zinc bath to improve the fluidity of the bath (thus limiting excess zinc on the dipped product by improved drainage properties), helps prevent floating dross, makes dross recycling easier and protects the Pilling kettle from uneven heat distribution from the burners. Lead is either added to primary Z1 grade zinc or already contained in used secondary zinc. A third, declining method is to use low Z5 grade zinc.
Steel strip can be hot-dip galvanized in a continuous line. Hot-dip galvanized steel strip (also sometimes loosely referred to as galvanized iron) is extensively used for applications requiring the strength of steel combined with the resistance to corrosion of zinc. roofing and walling, safety barriers, handrails, consumer appliances and automotive body parts. One common use is in metal pails. Galvanised steel is also used in most heating and cooling duct systems in buildings.
Individual metal articles, such as steel girders or wrought iron gates, can be hot-dip galvanized by a process called batch galvanizing. Other modern techniques have largely replaced hot-dip for these sorts of roles. This includes electrogalvanizing, which deposits the layer of zinc from an aqueous electrolyte by electroplating, forming a thinner and much stronger bond.
Packaging of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Strip
Shanghai Metal Products are packed and labeled according to the regulations and customer's requests. Great care is taken to avoid any damage which might be caused during storage or transportation. In addition, clear labels are tagged on the outside of the packages for easy identification of the product I. D. and quality information.
1) Shanghai Metal Standard
2) Customization
Applications of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Strip:
1) Construction and building: roofing, ventilating duct, handrail, partition panel, etc.
2) Further processing: coating base plate
3) Electric appliance: refrigerator, washing machine, recorder, microwave, etc.
What is Galvanized Steel?
There are two typical galvanizing ways to obtain a zinc coating: hot dip galvanizing and electrogalvanizing. Hot dip galvanizing is the process that steel is immersed into molten zinc bath to get a zinc coating surface. This not only helps protect steel from rust and corrosion, but also gives the steel a shiny attractive appearance. Electrogalvanizing is the process that uses electrolysis to coat the steel with zinc, which is neither cost-effective nor environmentally friendly. It is hardly to find electrogalvanized steel in our lives nowadays.
What are the advantages of Galvanized Steel?
Because of permanently and successive zinc/iron alloy layers, galvanized steel offers many benefits:
1) Corrosion Resistance: the zinc coating surface protects the base steel not only by providing barrier to corrosion elements, but also by the sacrificial nature of the coating. Galvanized steel often remains in working order with little maintenance for 40 years or more.
2) Excellent Surface Appearance
3) Formability: it can be simply bend to parts with deep drawing requirements
4) Paintability: it can be painted with different colors
5) Weldability: it is accepted various welding practices
What are the disadvantages of Galvanized Steel?
In spite of many benefits, galvanized steel is not always an ideal choice. Galvanized steel cannot be used underground without being properly covered, which can be inconvenient for many jobs.
Where do we use Galvanized Steel?
It is primarily used in the construction industry, such as roofing, wall cladding, and support beams. It is also used in the automotive industry, due to its enhanced paintability, weldability and corrosion resistance. Moreover, it is an essential material for white goods application, such as refrigerators, air-conditioners, washers, microwaves, vending machines and audio visual systems.
here
for
price






